
Security Report (DEMO)

Security Report (DEMO)
|
Site Name |
Start Time |
End Time |
Total Time |
Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Skylands Networks Demonstration Environment |
May 05, 2017 10:55, EDT |
May 05, 2017 11:03, EDT |
7 minutes |
Success |
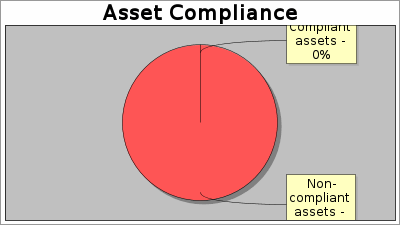
There is not enough historical data to display overall asset trend.
The audit was performed on 4 systems, 4 of which were found to be active and were scanned.
 |
 |
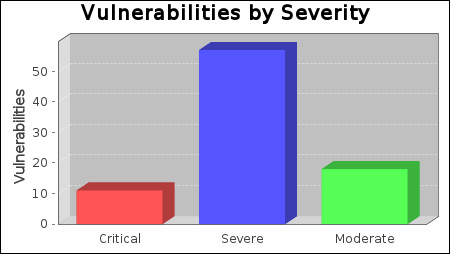
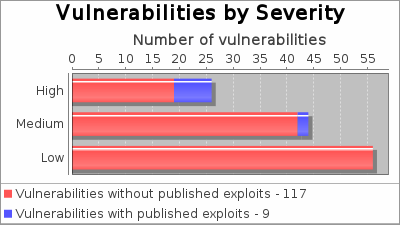
There were 86 vulnerabilities found during this scan. Of these, 11 were critical vulnerabilities. Critical vulnerabilities require immediate attention. They are relatively easy for attackers to exploit and may provide them with full control of the affected systems. 57 vulnerabilities were severe. Severe vulnerabilities are often harder to exploit and may not provide the same access to affected systems. There were 18 moderate vulnerabilities discovered. These often provide information to attackers that may assist them in mounting subsequent attacks on your network. These should also be fixed in a timely manner, but are not as urgent as the other vulnerabilities.
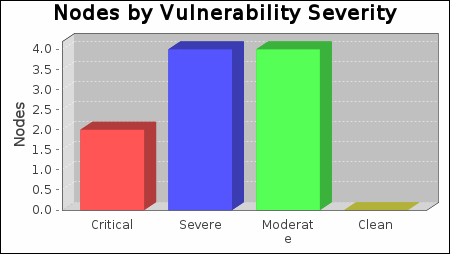
Critical vulnerabilities were found to exist on 2 of the systems, making them most susceptible to attack. 4 systems were found to have severe vulnerabilities. Moderate vulnerabilities were found on 4 systems. No systems were free of vulnerabilities.
 |
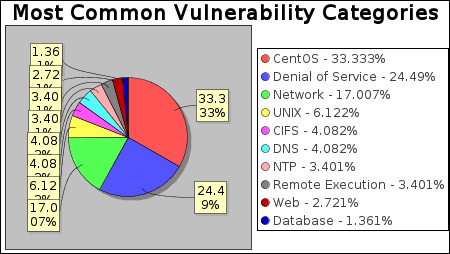 |
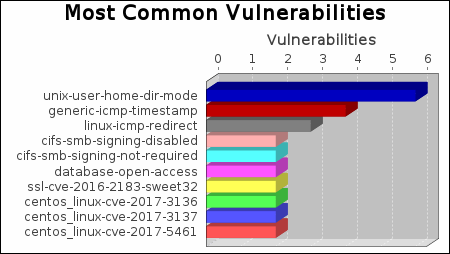
There were 6 occurrences of the unix-user-home-dir-mode vulnerability, making it the most common vulnerability. There were 49 vulnerability instances in the CentOS category, making it the most common vulnerability category.
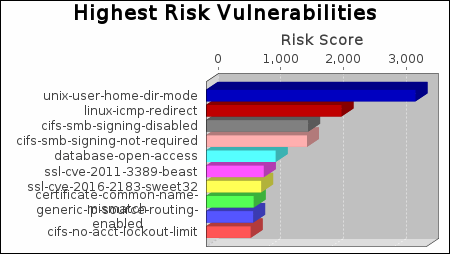 |
The unix-user-home-dir-mode vulnerability poses the highest risk to the organization with a risk score of 3,340. Risk scores are based on the types and numbers of vulnerabilities on affected assets.
There were 2 operating systems identified during this scan.
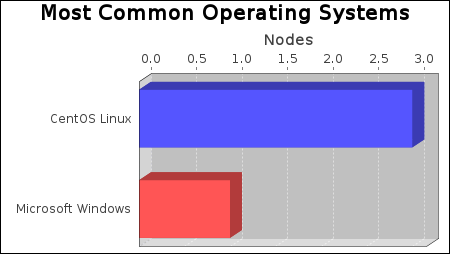 |
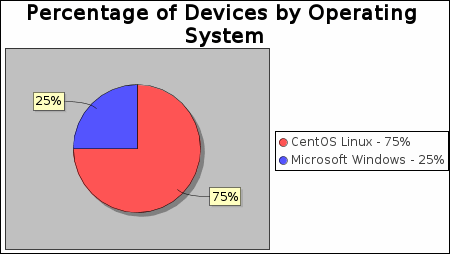 |
The CentOS Linux operating system was found on 3 systems, making it the most common operating system.
There were 11 services found to be running during this scan.
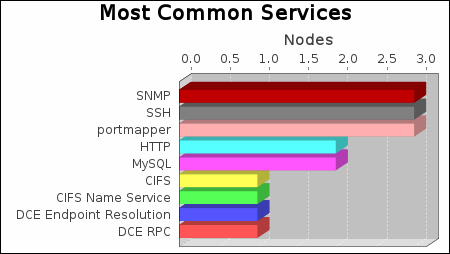 |
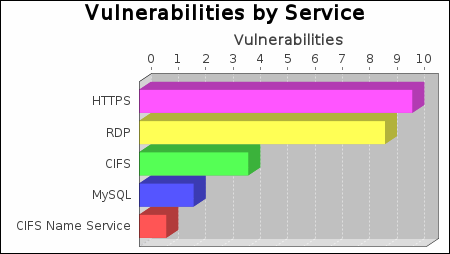 |
The SNMP, SSH and portmapper services were found on 3 systems, making them the most common services. The HTTPS service was found to have the most vulnerabilities during this scan with 10 vulnerabilities.
This report identifies security risks that could adversely affect your critical operations and assets. These risks are quantified according to their likelihood of occurrence and the potential damage if they occur. Risk factors are combined to form an overall risk index for each system, allowing you to prioritize your remediation activities accordingly.
Risk strategy: Real Risk. This strategy analyzes potential types of exposures associated with vulnerabilities to expand and deepen your understanding of real threats to your environment and the value of different mitigation approaches. The algorithm applies exploit and malware exposure metrics for each vulnerability to CVSS base metrics for asset impact (confidentiality, integrity, and availability) and likelihood of compromise (access vector, access complexity, and authentication requirements). It also indicates how time increases likelihood.
|
Device |
Risk Index |
Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|
|
192.168.1.30 (demo3) |
13,934 |
|
|
192.168.1.20 (demo2) |
5,728 |
|
|
192.168.1.10 (demo1) |
5,077 |
|
|
192.168.1.40 (demo4) |
1,832 |
|
CIFS, the Common Internet File System, was defined by Microsoft to provide file sharing services over the Internet. CIFS extends the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol designed by IBM and enhanced by Intel and Microsoft. CIFS provides mechanisms for sharing resources (files, printers, etc.) and executing remote procedure calls over named pipes.
|
Device |
Protocol |
Port |
Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
|
192.168.1.20 (demo2) |
tcp |
139 |
2 |
|
192.168.1.20 (demo2) |
tcp |
445 |
2 |
CIFS, the Common Internet File System, was defined by Microsoft to provide file sharing services over the Internet. CIFS extends the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol designed by IBM and enhanced by Intel and Microsoft. CIFS provides mechanisms for sharing resources (files, printers, etc.) and executing remote procedure calls over named pipes. This service is used to handle CIFS browsing (name) requests. Responses contain the names and types of services that can be accessed via CIFS named pipes.
|
Device |
Protocol |
Port |
Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
|
192.168.1.20 (demo2) |
udp |
137 |
1 |
The DCE Endpoint Resolution service, aka Endpoint Mapper, is used on Microsoft Windows systems by Remote Procedure Call (RPC) clients to determine the appropriate port number to connect to for a particular RPC service. This is similar to the portmapper service used on Unix systems.
|
Device |
Protocol |
Port |
Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
|
192.168.1.20 (demo2) |
tcp |
135 |
0 |
|
Device |
Protocol |
Port |
Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
|
192.168.1.20 (demo2) |
tcp |
49152 |
0 |
|
192.168.1.20 (demo2) |
tcp |
49153 |
0 |
|
192.168.1.20 (demo2) |
tcp |
49154 |
0 |
|
192.168.1.20 (demo2) |
tcp |
49174 |
0 |
|
192.168.1.20 (demo2) |
tcp |
49175 |
0 |
|
192.168.1.20 (demo2) |
tcp |
49179 |
0 |
HTTP, the HyperText Transfer Protocol, is used to exchange multimedia content on the World Wide Web. The multimedia files commonly used with HTTP include text, sound, images and video.
|
Device |
Protocol |
Port |
Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
|
192.168.1.10 (demo1) |
tcp |
80 |
0 |
|
192.168.1.30 (demo3) |
tcp |
80 |
0 |
HTTPS, the HyperText Transfer Protocol over TLS/SSL, is used to exchange multimedia content on the World Wide Web using encrypted (TLS/SSL) connections. Once the TLS/SSL connection is established, the standard HTTP protocol is used. The multimedia files commonly used with HTTP include text, sound, images and video.
|
Device |
Protocol |
Port |
Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
|
192.168.1.10 (demo1) |
tcp |
443 |
6 |
|
Device |
Protocol |
Port |
Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
|
192.168.1.40 (demo4) |
tcp |
3306 |
1 |
|
192.168.1.30 (demo3) |
tcp |
3306 |
1 |
|
Device |
Protocol |
Port |
Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
|
192.168.1.20 (demo2) |
tcp |
3389 |
4 |
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), like the name implies, is a simple protocol used to manage networking appliances by remote clients. It is primarily UDP-based and uses trivial authentication by means of a secret community name.
|
Device |
Protocol |
Port |
Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
|
192.168.1.40 (demo4) |
udp |
161 |
0 |
|
192.168.1.10 (demo1) |
udp |
161 |
0 |
|
192.168.1.30 (demo3) |
udp |
161 |
0 |
SSH, or Secure SHell, is designed to be a replacement for the aging Telnet protocol. It primarily adds encryption and data integrity to Telnet, but can also provide superior authentication mechanisms such as public key authentication.
|
Device |
Protocol |
Port |
Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
|
192.168.1.40 (demo4) |
tcp |
22 |
0 |
|
192.168.1.10 (demo1) |
tcp |
22 |
0 |
|
192.168.1.30 (demo3) |
tcp |
22 |
0 |
The Remote Procedure Call portmapper is a service that maps RPC programs to specific ports, and provides that information to client programs. Since most RPC programs do not have a well defined port number, they are dynamically allocated a port number when they are first run. Any client program that wishes to use a particular RPC program first contacts the portmapper to determine the port and protocol of the specified RPC program. The client then uses that information to contact the RPC program directly. In addition some implementations of the portmapper allow tunneling commands to RPC programs through the portmapper.
|
Device |
Protocol |
Port |
Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
|
192.168.1.40 (demo4) |
udp |
111 |
0 |
|
192.168.1.40 (demo4) |
tcp |
111 |
0 |
|
192.168.1.10 (demo1) |
udp |
111 |
0 |
|
192.168.1.10 (demo1) |
tcp |
111 |
0 |
|
192.168.1.30 (demo3) |
udp |
111 |
0 |
|
192.168.1.30 (demo3) |
tcp |
111 |
0 |
 |
 |
 |
|
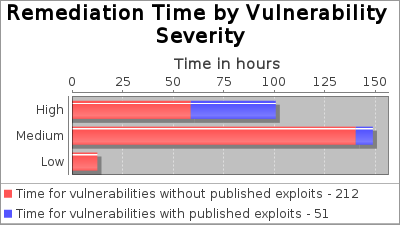
* An exploit is regarded as "published" if it is available from Metasploit or listed in the Exploit Database. Actual remediation times may differ based on organizational workflows. | ||
|
192.168.1.10 |
|
|
192.168.1.20 |
|
|
192.168.1.30 |
|
|
192.168.1.40 |
|
PCI Compliance Status |
|
|
Operating System |
CentOS Linux 7.3.1611 |
|
Aliases |
demo4 |
|
Vulnerability |
Instance |
Severity Level |
CVSS Score |
Compliance Status |
Evidence, Exceptions, False Positives, or Compensating Controls Noted by the ASV for this Vulnerability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Undefined CVE, ICMP redirection enabled |
medium |
6.8 |
| ||
| Undefined CVE, Database Open Access |
protocol: tcp port: 3306 |
medium |
5.0 |
| |
| Undefined CVE, User home directory mode unsafe |
low |
2.1 |
The permissions for home directory of user libstoragemgmt was found to be 775 instead of 750. | ||
| Undefined CVE, A service discloses version information |
protocol: tcp port: 22 instance: SSH |
low |
0.0 |
SSH on TCP port 22 running OpenSSH 6.6.1 | |
| Undefined CVE, A service discloses version information |
protocol: tcp port: 3306 instance: MySQL |
low |
0.0 |
MySQL on TCP port 3306 running MariaDB 5.5.52 | |
| CVE-1999-0524, ICMP timestamp response |
low |
0.0 |
Able to determine remote system time. | ||
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 22 instance: SSH |
low |
0.0 |
SSH on TCP port 22 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 111 instance: portmapper |
low |
0.0 |
portmapper on TCP port 111 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: udp port: 111 instance: portmapper |
low |
0.0 |
portmapper on UDP port 111 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: udp port: 161 instance: SNMP |
low |
0.0 |
SNMP on UDP port 161 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 3306 instance: MySQL |
low |
0.0 |
MySQL on TCP port 3306 | |
| Undefined CVE, TCP timestamp response |
low |
0.0 |
Acceptable Risk noted by admin: Disabling TCP timestamps can cause major issues. Google this if you need proof. |
These vulnerabilities can be resolved by performing the following 2 steps. The total estimated time to perform all of these steps is 40 minutes.
|
Remediation Step |
Estimated Time |
|---|---|
| Disable ICMP redirect support
Linux
Issue the following commands as root: sysctl -w net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects=0 sysctl -w net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_redirects=0 sysctl -w net.ipv4.conf.all.secure_redirects=0 sysctl -w net.ipv4.conf.default.secure_redirects=0 These settings can be added to /etc/sysctl.conf to make them permanent. |
10 minutes |
| Disable ICMP timestamp responses on Linux
Linux
Linux offers neither a sysctl nor a /proc/sys/net/ipv4 interface to disable ICMP timestamp responses. Therefore, you should block ICMP on the affected host using iptables, and/or block it at the firewall. For example: ipchains -A input -p icmp --icmp-type timestamp-request -j DROP ipchains -A output -p icmp --icmp-type timestamp-reply -j DROP The easiest and most effective solution is to configure your firewall to block incoming and outgoing ICMP packets with ICMP types 13 (timestamp request) and 14 (timestamp response). |
30 minutes |
These vulnerabilities can be resolved with a single step. The estimated time to perform this step is 30 minutes.
|
Remediation Step |
Estimated Time |
|---|---|
| Restrict database access
Configure the database server to only allow access to trusted systems. For example, the PCI DSS standard requires you to place the database in an internal network zone, segregated from the DMZ |
30 minutes |
These vulnerabilities can be resolved with a single step. The estimated time to perform this step is 1 minute.
|
Remediation Step |
Estimated Time |
|---|---|
| Restrict User's home directory mode
Restrict the user home directory mode to at most 750 using the command: chmod 750 userDir |
1 minute |
|
PCI Compliance Status |
|
|
Operating System |
CentOS Linux 7.3.1611 |
|
Aliases |
demo1 |
|
Vulnerability |
Instance |
Severity Level |
CVSS Score |
Compliance Status |
Evidence, Exceptions, False Positives, or Compensating Controls Noted by the ASV for this Vulnerability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Undefined CVE, X.509 Certificate Subject CN Does Not Match the Entity Name |
protocol: tcp port: 443 |
high |
7.1 |
The subject common name found in the X.509 certificate does not seem to match the scan target:
| |
| Undefined CVE, ICMP redirection enabled |
medium |
6.8 |
| ||
| Undefined CVE, Untrusted TLS/SSL server X.509 certificate |
protocol: tcp port: 443 |
medium |
5.8 |
TLS/SSL certificate signed by unknown, untrusted CA: CN=COMODO RSA Domain Validation Secure Server CA, O=COMODO CA Limited, L=Salford, ST=Greater Manchester, C=GB -- [basic constraints check failed: pathLenConstraint violated - this cert must be the last cert in the certification path, subject/issuer name chaining check failed, Path does not chain with any of the trust anchors]. | |
| CVE-2016-2183, TLS/SSL Birthday attacks on 64-bit block ciphers (SWEET32) |
protocol: tcp port: 443 |
medium |
5.0 |
| |
| CVE-2017-3136, CVE-2017-3137, CVE-2017-3138, Cent OS: CVE-2017-3136: CESA-2017:1105 (bind) |
medium |
4.4 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2017-3136, CVE-2017-3137, CVE-2017-3138, Cent OS: CVE-2017-3137: CESA-2017:1105 (bind) |
medium |
4.4 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2017-5461, Cent OS: CVE-2017-5461: CESA-2017:1100 (nss and nss-util) |
medium |
4.4 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2011-3389, TLS/SSL Server is enabling the BEAST attack |
protocol: tcp port: 443 |
medium |
4.3 |
| |
| Undefined CVE, TLS Server Supports TLS version 1.0 |
protocol: tcp port: 443 |
medium |
4.3 |
Successfully connected over TLSv1.0 | |
| Undefined CVE, TLS/SSL Server Supports The Use of Static Key Ciphers |
protocol: tcp port: 443 |
low |
2.6 |
| |
| Undefined CVE, Diffie-Hellman group smaller than 2048 bits |
protocol: tcp port: 443 |
low |
2.6 |
| |
| Undefined CVE, TLS/SSL Server Is Using Commonly Used Prime Numbers |
protocol: tcp port: 443 |
low |
2.6 |
| |
| Undefined CVE, TLS Server Supports TLS version 1.1 |
protocol: tcp port: 443 |
low |
2.6 |
Successfully connected over TLSv1.1 | |
| Undefined CVE, User home directory mode unsafe |
low |
2.1 |
The permissions for home directory of user nginx was found to be 755 instead of 750. | ||
| Undefined CVE, User home directory mode unsafe |
low |
2.1 |
The permissions for home directory of user mysql was found to be 755 instead of 750. | ||
| Undefined CVE, User home directory mode unsafe |
low |
2.1 |
The permissions for home directory of user libstoragemgmt was found to be 775 instead of 750. | ||
| Undefined CVE, A service discloses version information |
protocol: tcp port: 22 instance: SSH |
low |
0.0 |
SSH on TCP port 22 running OpenSSH 6.6.1 | |
| Undefined CVE, A service discloses version information |
protocol: tcp port: 80 instance: HTTP |
low |
0.0 |
HTTP on TCP port 80 running nginx 1.10.3 | |
| Undefined CVE, A service discloses version information |
protocol: tcp port: 443 instance: HTTPS |
low |
0.0 |
HTTPS on TCP port 443 running nginx 1.10.3 | |
| CVE-1999-0524, ICMP timestamp response |
low |
0.0 |
Able to determine remote system time. | ||
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 22 instance: SSH |
low |
0.0 |
SSH on TCP port 22 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 80 instance: HTTP |
low |
0.0 |
HTTP on TCP port 80 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 111 instance: portmapper |
low |
0.0 |
portmapper on TCP port 111 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: udp port: 111 instance: portmapper |
low |
0.0 |
portmapper on UDP port 111 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: udp port: 161 instance: SNMP |
low |
0.0 |
SNMP on UDP port 161 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 443 instance: HTTPS |
low |
0.0 |
HTTPS on TCP port 443 | |
| Undefined CVE, TCP timestamp response |
low |
0.0 |
Acceptable Risk noted by admin: Disabling TCP timestamps can cause major issues. Google this if you need proof. | ||
| Undefined CVE, TLS/SSL Server Supports 3DES Cipher Suite |
protocol: tcp port: 443 |
low |
0.0 |
|
These vulnerabilities can be resolved by performing the following 21 steps. The total estimated time to perform all of these steps is 10 hours 10 minutes.
|
Remediation Step |
Estimated Time |
|---|---|
| Upgrade bind-utils
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-utils to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-pkcs11-utils
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-pkcs11-utils to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-pkcs11
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-pkcs11 to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-license
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-license to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-sdb
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-sdb to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-pkcs11-libs
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-pkcs11-libs to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-pkcs11-devel
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-pkcs11-devel to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-sdb-chroot
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-sdb-chroot to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-libs
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-libs to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-devel
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-devel to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-libs-lite
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-libs-lite to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-chroot
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-chroot to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-lite-devel
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-lite-devel to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Disable ICMP redirect support
Linux
Issue the following commands as root: sysctl -w net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects=0 sysctl -w net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_redirects=0 sysctl -w net.ipv4.conf.all.secure_redirects=0 sysctl -w net.ipv4.conf.default.secure_redirects=0 These settings can be added to /etc/sysctl.conf to make them permanent. |
10 minutes |
| Upgrade nss-sysinit
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update nss-sysinit to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade nss-devel
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update nss-devel to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade nss
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update nss to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade nss-pkcs11-devel
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update nss-pkcs11-devel to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade nss-tools
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update nss-tools to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Disable ICMP timestamp responses on Linux
Linux
Linux offers neither a sysctl nor a /proc/sys/net/ipv4 interface to disable ICMP timestamp responses. Therefore, you should block ICMP on the affected host using iptables, and/or block it at the firewall. For example: ipchains -A input -p icmp --icmp-type timestamp-request -j DROP ipchains -A output -p icmp --icmp-type timestamp-reply -j DROP The easiest and most effective solution is to configure your firewall to block incoming and outgoing ICMP packets with ICMP types 13 (timestamp request) and 14 (timestamp response). |
30 minutes |
These vulnerabilities can be resolved by performing the following 8 steps. The total estimated time to perform all of these steps is 6 hours 55 minutes.
|
Remediation Step |
Estimated Time |
|---|---|
| Fix the subject's Common Name (CN) field in the certificate
The subject's common name (CN) field in the X.509 certificate should be fixed to reflect the name of the entity presenting the certificate (e.g., the hostname). This is done by generating a new certificate usually signed by a Certification Authority (CA) trusted by both the client and server. |
10 minutes |
| Disable insecure TLS/SSL protocol support
Configure the server to require clients to use TLS version 1.2 using Authenticated Encryption with Associated Data (AEAD) capable ciphers. |
1 hour |
| Obtain a new certificate from your CA and ensure the server configuration is correct
Ensure the common name (CN) reflects the name of the entity presenting the certificate (e.g., the hostname). If the certificate(s) or any of the chain certificate(s) have expired or been revoked, obtain a new certificate from your Certificate Authority (CA) by following their documentation. If a self-signed certificate is being used, consider obtaining a signed certificate from a CA. References: Mozilla: Connection Untrusted Error ( https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/connection-untrusted-error-message ) SSLShopper: SSL Certificate Not Trusted Error ( https://www.sslshopper.com/ssl-certificate-not-trusted-error.html ) Windows/IIS certificate chain config ( https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/954755 ) Apache SSL config ( http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.2/mod/mod_ssl.html ) Nginx SSL config ( http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/configuring_https_servers.html ) CertificateChain.io ( https://certificatechain.io/ ) |
1 hour 30 minutes |
| Disable TLS/SSL support for 3DES cipher suite
Configure the server to disable support for 3DES suite. For Microsoft IIS web servers, see Microsoft Knowledgebase article 245030 ( http://support.microsoft.com/kb/245030/ ) for instructions on disabling 3DES cipher suite. The following recommended configuration provides a higher level of security. This configuration is compatible with Firefox 27, Chrome 22, IE 11, Opera 14 and Safari 7. SSLv2, SSLv3, and TLSv1 protocols are not recommended in this configuration. Instead, use TLSv1.1 and TLSv1.2 protocols. Refer to your server vendor documentation to apply the recommended cipher configuration: ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-DSS-AES128-GCM-SHA256:kEDH+AESGCM:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:DHE-DSS-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256:DHE-DSS-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:!aNULL:!eNULL:!EXPORT:!DES:!RC4:!3DES:!MD5:!PSK |
1 hour |
| Disable SSLv2, SSLv3, and TLS 1.0. The best solution is to only have TLS 1.2 enabled
There is no server-side mitigation available against the BEAST attack. The only option is to disable the affected protocols (SSLv3 and TLS 1.0). The only fully safe configuration is to use Authenticated Encryption with Associated Data (AEAD), e.g. AES-GCM, AES-CCM in TLS 1.2. |
1 hour |
| Use a Stronger Diffie-Hellman Group
Please refer to this guide to deploying Diffie-Hellman for TLS ( https://weakdh.org/sysadmin.html ) for instructions on how to configure the server to use 2048-bit or stronger Diffie-Hellman groups with safe primes. |
15 minutes |
| Disable TLS/SSL support for static key cipher suites
Configure the server to disable support for static key cipher suites. For Microsoft IIS web servers, see Microsoft Knowledgebase article 245030 ( http://support.microsoft.com/kb/245030/ ) for instructions on disabling static key cipher suites. The following recommended configuration provides a higher level of security. This configuration is compatible with Firefox 27, Chrome 22, IE 11, Opera 14 and Safari 7. SSLv2, SSLv3, and TLSv1 protocols are not recommended in this configuration. Instead, use TLSv1.1 and TLSv1.2 protocols. Refer to your server vendor documentation to apply the recommended cipher configuration: ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-DSS-AES128-GCM-SHA256:kEDH+AESGCM:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:DHE-DSS-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256:DHE-DSS-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:!aNULL:!eNULL:!EXPORT:!DES:!RC4:!3DES:!MD5:!PSK |
1 hour |
| Generate random Diffie-Hellman parameters
Configure the server to use a randomly generated Diffie-Hellman group. It's recommend that you generate a 2048-bit group. The simplest way of generating a new group is to use OpenSSL: openssl dhparam -out dhparams.pem 2048 To use the DH parameters in newer versions of Apache (2.4.8 and newer) and OpenSSL 1.0.2 or later, you can directly specify your DH params file as follows: SSLOpenSSLConfCmd DHParameters "{path to dhparams.pem}" If you are using Apache with LibreSSL, or Apache 2.4.7 and OpenSSL 0.9.8a or later, you can append the DHparams you generated earlier to the end of your certificate file and reload the configuration. For other products see the remediation steps suggested by the original researchers. ( https://weakdh.org/sysadmin.html ) |
1 hour |
These vulnerabilities can be resolved with a single step. The estimated time to perform this step is 3 minutes.
|
Remediation Step |
Estimated Time |
|---|---|
| Restrict User's home directory mode
Restrict the user home directory mode to at most 750 using the command: chmod 750 userDir |
3 minutes |
|
PCI Compliance Status |
|
|
Operating System |
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2, Enterprise Edition SP1 |
|
Aliases |
demo2 |
|
Vulnerability |
Instance |
Severity Level |
CVSS Score |
Compliance Status |
Evidence, Exceptions, False Positives, or Compensating Controls Noted by the ASV for this Vulnerability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-1999-0510, CVE-1999-0909, IP Source Routing Enabled |
high |
7.5 |
Vulnerable OS: Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2, Enterprise Edition SP1
| ||
| Undefined CVE, SMB signing disabled |
protocol: tcp port: 139 |
high |
7.3 |
Negotiate protocol response's security mode 3 indicates that SMB signing is disabled | |
| Undefined CVE, SMB signing disabled |
protocol: tcp port: 445 |
high |
7.3 |
Negotiate protocol response's security mode 3 indicates that SMB signing is disabled | |
| CVE-2017-0160, Microsoft CVE-2017-0160: .NET Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
high |
7.2 |
Vulnerable software installed: Microsoft .NET Framework 4.5.2 Vulnerable OS: Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2, Enterprise Edition SP1
| ||
| Undefined CVE, CIFS Account Lockout Policy Not Enforced |
instance: Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2, Enterprise Edition SP1 |
medium |
6.8 |
Vulnerable OS: Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2, Enterprise Edition SP1
| |
| Undefined CVE, SMB signing not required |
protocol: tcp port: 139 |
medium |
6.2 |
Negotiate protocol response's security mode 3 indicates that SMB signing is not required | |
| Undefined CVE, SMB signing not required |
protocol: tcp port: 445 |
medium |
6.2 |
Negotiate protocol response's security mode 3 indicates that SMB signing is not required | |
| CVE-2016-2183, TLS/SSL Birthday attacks on 64-bit block ciphers (SWEET32) |
protocol: tcp port: 3389 |
medium |
5.0 |
| |
| CVE-2013-2566, TLS/SSL Server Supports RC4 Cipher Algorithms (CVE-2013-2566) |
protocol: tcp port: 3389 |
medium |
4.3 |
| |
| CVE-2011-3389, TLS/SSL Server is enabling the BEAST attack |
protocol: tcp port: 3389 |
medium |
4.3 |
| |
| Undefined CVE, TLS Server Supports TLS version 1.0 |
protocol: tcp port: 3389 |
medium |
4.3 |
Successfully connected over TLSv1.0 | |
| Undefined CVE, TLS/SSL Server Supports The Use of Static Key Ciphers |
protocol: tcp port: 3389 |
low |
2.6 |
| |
| Undefined CVE, Diffie-Hellman group smaller than 2048 bits |
protocol: tcp port: 3389 |
low |
2.6 |
| |
| Undefined CVE, TLS/SSL Server Is Using Commonly Used Prime Numbers |
protocol: tcp port: 3389 |
low |
2.6 |
| |
| Undefined CVE, TLS Server Supports TLS version 1.1 |
protocol: tcp port: 3389 |
low |
2.6 |
Successfully connected over TLSv1.1 | |
| CVE-1999-0524, ICMP timestamp response |
low |
0.0 |
Able to determine remote system time. | ||
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 135 instance: DCE Endpoint Resolution |
low |
0.0 |
DCE Endpoint Resolution on TCP port 135 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: udp port: 137 instance: CIFS Name Service |
low |
0.0 |
CIFS Name Service on UDP port 137 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 139 instance: CIFS |
low |
0.0 |
CIFS on TCP port 139 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 445 instance: CIFS |
low |
0.0 |
CIFS on TCP port 445 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 3389 instance: RDP |
low |
0.0 |
RDP on TCP port 3389 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 49152 instance: DCE RPC |
low |
0.0 |
DCE RPC on TCP port 49152 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 49153 instance: DCE RPC |
low |
0.0 |
DCE RPC on TCP port 49153 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 49154 instance: DCE RPC |
low |
0.0 |
DCE RPC on TCP port 49154 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 49174 instance: DCE RPC |
low |
0.0 |
DCE RPC on TCP port 49174 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 49175 instance: DCE RPC |
low |
0.0 |
DCE RPC on TCP port 49175 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 49179 instance: DCE RPC |
low |
0.0 |
DCE RPC on TCP port 49179 | |
| Undefined CVE, TCP timestamp response |
low |
0.0 |
Acceptable Risk noted by admin: Disabling TCP timestamps can cause major issues. Google this if you need proof. | ||
| Undefined CVE, NetBIOS NBSTAT Traffic Amplification |
protocol: udp port: 137 |
low |
0.0 |
| |
| Undefined CVE, TLS/SSL Server Supports 3DES Cipher Suite |
protocol: tcp port: 3389 |
low |
0.0 |
|
These vulnerabilities can be resolved by performing the following 2 steps. The total estimated time to perform all of these steps is 45 minutes.
|
Remediation Step |
Estimated Time |
|---|---|
| Configure SMB signing for Windows
Microsoft Windows
Configure the system to enable or require SMB signing as appropriate. The method and effect of doing this is system specific so please see this TechNet article ( http://blogs.technet.com/b/josebda/archive/2010/12/01/the-basics-of-smb-signing-covering-both-smb1-and-smb2.aspx ) for details. Note: ensure that SMB signing configuration is done for incoming connections (Server). |
30 minutes |
| Set an account lockout threshold for Windows Vista/2008 and newer
Microsoft Windows Vista, Microsoft Windows Vista Home, Basic Edition, Microsoft Windows Vista Home, Basic N Edition, Microsoft Windows Vista Home, Premium Edition, Microsoft Windows Vista Ultimate Edition, Microsoft Windows Vista Enterprise Edition, Microsoft Windows Vista Business Edition, Microsoft Windows Vista Business N Edition, Microsoft Windows Vista Starter Edition, Microsoft Windows Server 2008, Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Standard Edition, Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Edition, Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Datacenter Edition, Microsoft Windows Server 2008 HPC Edition, Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Web Edition, Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Storage Edition, Microsoft Windows Small Business Server 2008, Microsoft Windows Essential Business Server 2008, Microsoft Windows Server 2012, Microsoft Windows Server 2012 Essentials Edition, Microsoft Windows Server 2012 Standard Edition, Microsoft Windows Server 2012 Datacenter Edition, Microsoft Windows Server 2012 Foundation Edition, Microsoft Windows Storage Server 2012, Microsoft Windows 7, Microsoft Windows 7 Home, Basic Edition, Microsoft Windows 7 Home, Basic N Edition, Microsoft Windows 7 Home, Premium Edition, Microsoft Windows 7 Home, Premium N Edition, Microsoft Windows 7 Ultimate Edition, Microsoft Windows 7 Ultimate N Edition, Microsoft Windows 7 Enterprise Edition, Microsoft Windows 7 Enterprise N Edition, Microsoft Windows 7 Professional Edition, Microsoft Windows 7 Starter Edition, Microsoft Windows 7 Starter N Edition, Microsoft Windows Embedded Standard 7, Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2, Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2, Enterprise Edition, Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2, Standard Edition, Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2, Datacenter Edition, Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2, Web Edition, Microsoft Windows 8, Microsoft Windows 8 Enterprise Edition, Microsoft Windows 8 Professional Edition, Microsoft Windows RT
|
15 minutes |
These vulnerabilities can be resolved by performing the following 7 steps. The total estimated time to perform all of these steps is 6 hours 15 minutes.
|
Remediation Step |
Estimated Time |
|---|---|
| Disable insecure TLS/SSL protocol support
Configure the server to require clients to use TLS version 1.2 using Authenticated Encryption with Associated Data (AEAD) capable ciphers. |
1 hour |
| Disable TLS/SSL support for 3DES cipher suite
Configure the server to disable support for 3DES suite. For Microsoft IIS web servers, see Microsoft Knowledgebase article 245030 ( http://support.microsoft.com/kb/245030/ ) for instructions on disabling 3DES cipher suite. The following recommended configuration provides a higher level of security. This configuration is compatible with Firefox 27, Chrome 22, IE 11, Opera 14 and Safari 7. SSLv2, SSLv3, and TLSv1 protocols are not recommended in this configuration. Instead, use TLSv1.1 and TLSv1.2 protocols. Refer to your server vendor documentation to apply the recommended cipher configuration: ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-DSS-AES128-GCM-SHA256:kEDH+AESGCM:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:DHE-DSS-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256:DHE-DSS-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:!aNULL:!eNULL:!EXPORT:!DES:!RC4:!3DES:!MD5:!PSK |
1 hour |
| Disable SSLv2, SSLv3, and TLS 1.0. The best solution is to only have TLS 1.2 enabled
There is no server-side mitigation available against the BEAST attack. The only option is to disable the affected protocols (SSLv3 and TLS 1.0). The only fully safe configuration is to use Authenticated Encryption with Associated Data (AEAD), e.g. AES-GCM, AES-CCM in TLS 1.2. |
1 hour |
| Disable TLS/SSL support for RC4 ciphers
Configure the server to disable support for RC4 ciphers. For Microsoft IIS web servers, see Microsoft Knowledgebase article 245030 ( http://support.microsoft.com/kb/245030/ ) for instructions on disabling rc4 ciphers. The following recommended configuration provides a higher level of security. This configuration is compatible with Firefox 27, Chrome 22, IE 11, Opera 14 and Safari 7. SSLv2, SSLv3, and TLSv1 protocols are not recommended in this configuration. Instead, use TLSv1.1 and TLSv1.2 protocols. Refer to your server vendor documentation to apply the recommended cipher configuration: ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-DSS-AES128-GCM-SHA256:kEDH+AESGCM:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:DHE-DSS-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256:DHE-DSS-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:!aNULL:!eNULL:!EXPORT:!DES:!RC4:!3DES:!MD5:!PSK |
1 hour |
| Use a Stronger Diffie-Hellman Group
Please refer to this guide to deploying Diffie-Hellman for TLS ( https://weakdh.org/sysadmin.html ) for instructions on how to configure the server to use 2048-bit or stronger Diffie-Hellman groups with safe primes. |
15 minutes |
| Disable TLS/SSL support for static key cipher suites
Configure the server to disable support for static key cipher suites. For Microsoft IIS web servers, see Microsoft Knowledgebase article 245030 ( http://support.microsoft.com/kb/245030/ ) for instructions on disabling static key cipher suites. The following recommended configuration provides a higher level of security. This configuration is compatible with Firefox 27, Chrome 22, IE 11, Opera 14 and Safari 7. SSLv2, SSLv3, and TLSv1 protocols are not recommended in this configuration. Instead, use TLSv1.1 and TLSv1.2 protocols. Refer to your server vendor documentation to apply the recommended cipher configuration: ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-DSS-AES128-GCM-SHA256:kEDH+AESGCM:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:DHE-DSS-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256:DHE-DSS-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:!aNULL:!eNULL:!EXPORT:!DES:!RC4:!3DES:!MD5:!PSK |
1 hour |
| Generate random Diffie-Hellman parameters
Configure the server to use a randomly generated Diffie-Hellman group. It's recommend that you generate a 2048-bit group. The simplest way of generating a new group is to use OpenSSL: openssl dhparam -out dhparams.pem 2048 To use the DH parameters in newer versions of Apache (2.4.8 and newer) and OpenSSL 1.0.2 or later, you can directly specify your DH params file as follows: SSLOpenSSLConfCmd DHParameters "{path to dhparams.pem}" If you are using Apache with LibreSSL, or Apache 2.4.7 and OpenSSL 0.9.8a or later, you can append the DHparams you generated earlier to the end of your certificate file and reload the configuration. For other products see the remediation steps suggested by the original researchers. ( https://weakdh.org/sysadmin.html ) |
1 hour |
These vulnerabilities can be resolved by performing the following 2 steps. The total estimated time to perform all of these steps is 40 minutes.
|
Remediation Step |
Estimated Time |
|---|---|
| April, 2017 Security Only Update for .NET Framework 4.5.2 on Windows Embedded 8 Standard for x64 (KB4014986) ( http://support.microsoft.com/kb/4014986 ) |
20 minutes |
| April, 2017 Security Only Update for .NET Framework 4.5.2 on Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 for x64 (KB4014985) ( http://support.microsoft.com/kb/4014985 ) |
20 minutes |
These vulnerabilities can be resolved by performing the following 2 steps. The total estimated time to perform all of these steps is 40 minutes.
|
Remediation Step |
Estimated Time |
|---|---|
| April, 2017 Security Only Update for .NET Framework 3.5 on Windows Embedded 8 Standard for x64 (KB4014986) ( http://support.microsoft.com/kb/4014986 ) |
20 minutes |
| April, 2017 Security Only Update for .NET Framework 3.5.1 on Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 for x64 (KB4014985) ( http://support.microsoft.com/kb/4014985 ) |
20 minutes |
These vulnerabilities can be resolved by performing the following 2 steps. The total estimated time to perform all of these steps is 45 minutes.
|
Remediation Step |
Estimated Time |
|---|---|
| Disable IP source routing
Disable IP source routing on your operating system. For Windows systems ensure the following registry keys are set:
For Linux systems ensure the following sysctl values are set:
More Linux information can be found at https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/6/html/Security_Guide/sect-Security_Guide-Server_Security-Disable-Source-Routing.html |
15 minutes |
| Disable ICMP timestamp responses
Disable ICMP timestamp replies for the device. If the device does not support this level of configuration, the easiest and most effective solution is to configure your firewall to block incoming and outgoing ICMP packets with ICMP types 13 (timestamp request) and 14 (timestamp response). |
30 minutes |
These vulnerabilities can be resolved with a single step. The estimated time to perform this step is 2 hours.
|
Remediation Step |
Estimated Time |
|---|---|
| Restrict access to NetBIOS
NetBIOS can be important to the proper functioning of a Windows network depending on the design. Restrict access to the NetBIOS service to only trusted assets. |
2 hours |
|
PCI Compliance Status |
|
|
Operating System |
CentOS Linux 7.3.1611 |
|
Aliases |
demo3 |
|
Vulnerability |
Instance |
Severity Level |
CVSS Score |
Compliance Status |
Evidence, Exceptions, False Positives, or Compensating Controls Noted by the ASV for this Vulnerability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2016-7117, Cent OS: CVE-2016-7117: CESA-2017:0086 (kernel) |
high |
10.0 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-9555, Cent OS: CVE-2016-9555: CESA-2017:0307 (kernel) |
high |
10.0 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-7039, Cent OS: CVE-2016-7039: CESA-2016:2047 (kernel) |
high |
7.8 |
DoS-only vulnerability marked as compliant. | ||
| CVE-2016-6786, CVE-2016-6787, CVE-2016-8405, CVE-2016-9191, CVE-2017-2583, CVE-2017-2584, CVE-2017-2596, CVE-2017-2618, CVE-2017-5549, CVE-2017-5551, CVE-2017-5897, CVE-2017-5970, CVE-2017-6001, CVE-2017-6074, Cent OS: CVE-2017-2618: CESA-2017:0933 (kernel) |
high |
7.6 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-9533, Cent OS: CVE-2016-9533: CESA-2017:0225 (libtiff) |
high |
7.5 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-9534, Cent OS: CVE-2016-9534: CESA-2017:0225 (libtiff) |
high |
7.5 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-9535, Cent OS: CVE-2016-9535: CESA-2017:0225 (libtiff) |
high |
7.5 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-9536, Cent OS: CVE-2016-9536: CESA-2017:0225 (libtiff) |
high |
7.5 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-9537, Cent OS: CVE-2016-9537: CESA-2017:0225 (libtiff) |
high |
7.5 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-9540, Cent OS: CVE-2016-9540: CESA-2017:0225 (libtiff) |
high |
7.5 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2015-8660, Cent OS: CVE-2015-8660: CESA-2016:1539 (kernel) |
high |
7.2 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-3134, Cent OS: CVE-2016-3134: CESA-2016:1847 (kernel) |
high |
7.2 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-4565, Cent OS: CVE-2016-4565: CESA-2016:1406 (kernel) |
high |
7.2 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-4997, Cent OS: CVE-2016-4997: CESA-2016:1847 (kernel) |
high |
7.2 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-5195, Cent OS: CVE-2016-5195: CESA-2016:2124 (kernel) |
high |
7.2 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-8655, Cent OS: CVE-2016-8655: CESA-2017:0386 (kernel) |
high |
7.2 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-9083, Cent OS: CVE-2016-9083: CESA-2017:0386 (kernel) |
high |
7.2 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-9793, Cent OS: CVE-2016-9793: CESA-2017:0933 (kernel) |
high |
7.2 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2017-2636, Cent OS: CVE-2017-2636: CESA-2017:0933 (kernel) |
high |
7.2 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2017-6074, Cent OS: CVE-2017-6074: CESA-2017:0323 (kernel) |
high |
7.2 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-9311, Cent OS: CVE-2016-9311: CESA-2017:0252 (ntp) |
high |
7.1 |
DoS-only vulnerability marked as compliant. | ||
| Undefined CVE, Cent OS: CVE-2016-2143: CESA-2016:2766 (kernel) |
medium |
6.9 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-5652, Cent OS: CVE-2016-5652: CESA-2017:0225 (libtiff) |
medium |
6.8 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| Undefined CVE, ICMP redirection enabled |
medium |
6.8 |
| ||
| CVE-2016-9310, Cent OS: CVE-2016-9310: CESA-2017:0252 (ntp) |
medium |
6.4 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2015-8870, Cent OS: CVE-2015-8870: CESA-2017:0225 (libtiff) |
medium |
5.8 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-5696, Cent OS: CVE-2016-5696: CESA-2016:1664 (kernel) |
medium |
5.8 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-4998, Cent OS: CVE-2016-4998: CESA-2017:0036 (kernel) |
medium |
5.6 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| Undefined CVE, Database Open Access |
protocol: tcp port: 3306 |
medium |
5.0 |
| |
| CVE-2015-8767, Cent OS: CVE-2015-8767: CESA-2016:1277 (kernel) |
medium |
5.0 |
DoS-only vulnerability marked as compliant. | ||
| CVE-2016-7433, Cent OS: CVE-2016-7433: CESA-2017:0252 (ntp) |
medium |
5.0 |
DoS-only vulnerability marked as compliant. | ||
| CVE-2016-9131, Cent OS: CVE-2016-9131: CESA-2017:0062 (bind) |
medium |
5.0 |
DoS-only vulnerability marked as compliant. | ||
| CVE-2016-9147, Cent OS: CVE-2016-9147: CESA-2017:0064 (bind97) |
medium |
5.0 |
DoS-only vulnerability marked as compliant. | ||
| CVE-2016-9444, Cent OS: CVE-2016-9444: CESA-2017:0062 (bind) |
medium |
5.0 |
DoS-only vulnerability marked as compliant. | ||
| CVE-2016-4470, Cent OS: CVE-2016-4470: CESA-2016:2006 (kernel) |
medium |
4.9 |
DoS-only vulnerability marked as compliant. | ||
| CVE-2016-6828, Cent OS: CVE-2016-6828: CESA-2017:0086 (kernel) |
medium |
4.9 |
DoS-only vulnerability marked as compliant. | ||
| CVE-2016-8630, Cent OS: CVE-2016-8630: CESA-2017:0386 (kernel) |
medium |
4.9 |
DoS-only vulnerability marked as compliant. | ||
| CVE-2016-8650, Cent OS: CVE-2016-8650: CESA-2017:0933 (kernel) |
medium |
4.9 |
DoS-only vulnerability marked as compliant. | ||
| CVE-2016-9084, Cent OS: CVE-2016-9084: CESA-2017:0386 (kernel) |
medium |
4.6 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-8610, Cent OS: CVE-2016-8610: CESA-2017:0286 (openssl) |
medium |
4.4 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2017-2616, Cent OS: CVE-2017-2616: CESA-2017:0907 (util-linux) |
medium |
4.4 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2017-3135, Cent OS: CVE-2017-3135: CESA-2017:0276 (bind) |
medium |
4.4 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2017-3136, CVE-2017-3137, CVE-2017-3138, Cent OS: CVE-2017-3136: CESA-2017:1105 (bind) |
medium |
4.4 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2017-3136, CVE-2017-3137, CVE-2017-3138, Cent OS: CVE-2017-3137: CESA-2017:1105 (bind) |
medium |
4.4 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-7055, CVE-2017-3730, CVE-2017-3731, CVE-2017-3732, Cent OS: CVE-2017-3731: CESA-2017:0286 (openssl) |
medium |
4.4 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2017-5461, Cent OS: CVE-2017-5461: CESA-2017:1100 (nss and nss-util) |
medium |
4.4 |
Vulnerable OS: CentOS Linux 7.3.1611
| ||
| CVE-2016-7426, Cent OS: CVE-2016-7426: CESA-2017:0252 (ntp) |
medium |
4.3 |
DoS-only vulnerability marked as compliant. | ||
| CVE-2016-7429, Cent OS: CVE-2016-7429: CESA-2017:0252 (ntp) |
medium |
4.3 |
DoS-only vulnerability marked as compliant. | ||
| Undefined CVE, User home directory mode unsafe |
low |
2.1 |
The permissions for home directory of user nginx was found to be 755 instead of 750. | ||
| Undefined CVE, User home directory mode unsafe |
low |
2.1 |
The permissions for home directory of user libstoragemgmt was found to be 775 instead of 750. | ||
| Undefined CVE, A service discloses version information |
protocol: tcp port: 22 instance: SSH |
low |
0.0 |
SSH on TCP port 22 running OpenSSH 6.6.1 | |
| Undefined CVE, A service discloses version information |
protocol: tcp port: 80 instance: HTTP |
low |
0.0 |
HTTP on TCP port 80 running nginx 1.10.2 | |
| CVE-1999-0524, ICMP timestamp response |
low |
0.0 |
Able to determine remote system time. | ||
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 22 instance: SSH |
low |
0.0 |
SSH on TCP port 22 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 80 instance: HTTP |
low |
0.0 |
HTTP on TCP port 80 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 111 instance: portmapper |
low |
0.0 |
portmapper on TCP port 111 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: udp port: 111 instance: portmapper |
low |
0.0 |
portmapper on UDP port 111 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: udp port: 161 instance: SNMP |
low |
0.0 |
SNMP on UDP port 161 | |
| Undefined CVE, A running service was discovered |
protocol: tcp port: 3306 instance: MySQL |
low |
0.0 |
MySQL on TCP port 3306 | |
| Undefined CVE, TCP timestamp response |
low |
0.0 |
Acceptable Risk noted by admin: Disabling TCP timestamps can cause major issues. Google this if you need proof. |
These vulnerabilities can be resolved by performing the following 55 steps. The total estimated time to perform all of these steps is 27 hours 10 minutes.
|
Remediation Step |
Estimated Time |
|---|---|
| Upgrade kernel
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update kernel to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade kernel-tools-libs
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update kernel-tools-libs to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade kernel-devel
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update kernel-devel to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade kernel-tools-libs-devel
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update kernel-tools-libs-devel to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade kernel-tools
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update kernel-tools to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade kernel-headers
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update kernel-headers to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade kernel-debug-devel
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update kernel-debug-devel to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade kernel-doc
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update kernel-doc to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade kernel-debug
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update kernel-debug to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade python-perf
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update python-perf to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade perf
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update perf to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade kernel-abi-whitelists
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update kernel-abi-whitelists to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade libtiff-static
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update libtiff-static to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade libtiff
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update libtiff to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade libtiff-tools
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update libtiff-tools to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade libtiff-devel
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update libtiff-devel to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-libs
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-libs to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-pkcs11
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-pkcs11 to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-libs-lite
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-libs-lite to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-devel
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-devel to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-pkcs11-libs
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-pkcs11-libs to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-pkcs11-utils
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-pkcs11-utils to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-utils
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-utils to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-lite-devel
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-lite-devel to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-sdb
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-sdb to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-license
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-license to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-pkcs11-devel
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-pkcs11-devel to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-sdb-chroot
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-sdb-chroot to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade bind-chroot
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update bind-chroot to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade sntp
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update sntp to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade ntpdate
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update ntpdate to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade ntp
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update ntp to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade ntp-perl
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update ntp-perl to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade ntp-doc
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update ntp-doc to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade openssl-devel
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update openssl-devel to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade openssl-perl
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update openssl-perl to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade openssl
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update openssl to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade openssl-libs
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update openssl-libs to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade openssl-static
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update openssl-static to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Disable ICMP redirect support
Linux
Issue the following commands as root: sysctl -w net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects=0 sysctl -w net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_redirects=0 sysctl -w net.ipv4.conf.all.secure_redirects=0 sysctl -w net.ipv4.conf.default.secure_redirects=0 These settings can be added to /etc/sysctl.conf to make them permanent. |
10 minutes |
| Upgrade nss-pkcs11-devel
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update nss-pkcs11-devel to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade nss-devel
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update nss-devel to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade libuuid
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update libuuid to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade libmount-devel
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update libmount-devel to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade nss-sysinit
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update nss-sysinit to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade libmount
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update libmount to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade libblkid
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update libblkid to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade uuidd
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update uuidd to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade nss
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update nss to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade libblkid-devel
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update libblkid-devel to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade util-linux
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update util-linux to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade nss-tools
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update nss-tools to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Upgrade libuuid-devel
CentOS Linux 7.* (x86_64)
Update libuuid-devel to the latest version available from CentOS, using tools like yum or up2date. |
30 minutes |
| Disable ICMP timestamp responses on Linux
Linux
Linux offers neither a sysctl nor a /proc/sys/net/ipv4 interface to disable ICMP timestamp responses. Therefore, you should block ICMP on the affected host using iptables, and/or block it at the firewall. For example: ipchains -A input -p icmp --icmp-type timestamp-request -j DROP ipchains -A output -p icmp --icmp-type timestamp-reply -j DROP The easiest and most effective solution is to configure your firewall to block incoming and outgoing ICMP packets with ICMP types 13 (timestamp request) and 14 (timestamp response). |
30 minutes |
These vulnerabilities can be resolved with a single step. The estimated time to perform this step is 30 minutes.
|
Remediation Step |
Estimated Time |
|---|---|
| Restrict database access
Configure the database server to only allow access to trusted systems. For example, the PCI DSS standard requires you to place the database in an internal network zone, segregated from the DMZ |
30 minutes |
These vulnerabilities can be resolved with a single step. The estimated time to perform this step is 2 minutes.
|
Remediation Step |
Estimated Time |
|---|---|
| Restrict User's home directory mode
Restrict the user home directory mode to at most 750 using the command: chmod 750 userDir |
2 minutes |